Step by Step Describe the Consequences of P53 Gene Mutation
When this gene would be transcribed the nucleotide sequence of mRNA would also be changed. In most cases the p53 gene is mutated giving rise to a stable mutant protein whose accumulation is regarded as a hallmark of cancer cells.
Primary Information Of P53 Gene
The tumor suppressor gene p53 has been identified as the most frequent target of genetic alterations in human cancers.

. The more defective the mutation the greater the risk. This altered p53 protein cannot regulate cell growth and division and is unable to trigger apoptosis in cells with mutated or damaged DNA. Most of these mutations occur in highly conserved regions in the DNA-binding core domain of the p53 protein suggesting that the amino acid residues in these regions are critical for maintaining normal p53 structure and function.
Describe starting from transcription to translation to activation ending with function how this protein s shape and function could come out different abnormal after a change in p53 DNA sequence. The major consequences of gain of functions mutant p53 affect the metabolism and the response to oxidative stress of cancer cells. In most cases the p53 gene is mutated giving rise to a stable mutant protein whose accumulation is regarded as a hallmark of cancer cells.
Wild-type p53 regulates gene expression by directly binding to DNA in a sequence-specific manner. One-third of these p53 mutations are structural resulting in mutants with disrupted protein conformations. The essay should focus on the following discussion points.
Describe starting from transcription to translation to activation ending with function how this proteins shape and function could come out differentabnormal after a change in p53 DNA sequence. In the past fifteen years it has become apparent that tumour-associated p53 mutations can provoke activities that are different to those resulting from simply loss of wild-type tumour-suppressing p53 function. The molecular epidemiology of p53 mutations allows the possibility of correlating particular mutations with specific environmental carcinogens and establishing one step in the causal pathway between exposure to carcinogens and the development of cancer.
Inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor is a frequent event in tumorigenesis. The more defective the mutation the greater the risk. Step by step describe the consequences of p53 gene mutation.
Mutant p53 proteins not only lose their tumor suppressive activities but often gain additional oncogenic functions that endow cells with growth and survival advantages. After various types of genotoxic insults p53 is stabilized translocates to the nucleus and binds as a dimer of dimers to its response element RE McLure and Lee 1998. The p53 protein made by the TP53 gene normally acts as the supervisor in the cell as the body tries to repair damaged DNA.
A striking example is the G T transversion at the third base pair of codon 249 observed in liver cancer. First things first the mutation would change the nucleotide sequence of double stranded DNA. As a result DNA damage can accumulate in cells.
Interestingly mutations in the p53 gene were shown to. Rapid cell proliferation strongly needs of a ready supply of energy and basic macromolecules so mutant p53 proteins have been reported to facilitate the supply of cancer cells. Here we review current progress in p53-targeted drug development.
Step by step describe the consequences of p53 gene mutation. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. P53 is a transcription factor that activates many genes involved in essential maintenance of genetic stability.
The effects of DNA mutations within the p53 gene on the structure and function of the protein encoded by the gene. Most people that get cancer actually have both of their p53 gene copies mutated just from random chance. This aids in the suppression of cancer or tumors and any mutation in the p53 gene may reverse the tumors mutation and lead to aberrant cell proliferation resulting in tumor development or cancer.
Step by step describe the consequence of p53 gene mutation. Known mutations of the gene. The normal functions of the p53 gene.
P53 is the most frequently mutated gene in human cancers. If there is a mutation in the gene sequence that code for p53 then there can be grave consequences. Germline mutations in the TP53 gene are uncommon and associated with a specific cancer syndrome known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Your cells make these accidental mutations all the when a cell is making more copies of itself. The impact of mutations on the structure of the protein encoded by the gene. The first step in p53-mediated transcription is the binding of the protein to its recognition site in DNA.
We just have to hope it doesnt make the mistake in p53. When TP53 mutations are inherited they cause LFS a disease that leaves people with a 90 percent chance of developing cancer in their lifetime. Mutant p53 proteins not only lose their tumor suppressive activities but often gain additional oncogenic functions that endow cells with growth and survival advantages.
P53 is a tumor protein that regulates the cell cycle and aids in the tumor suppression process. How can it leaf to. People with Li-Fraumeni syndrome often develop cancer as children or young adults and the germline mutation is associated with a high lifetime risk of cancers such as breast cancer bone cancer muscle cancer and more.
Most of these mutations change single amino acids in p53. Describe starting from transcription to translation to activation ending with function how this proteins shape and function could come out differentabnormal after a change in p53 DNA sequence. When TP53 mutations are inherited they cause LFS a disease that leaves people with a 90 percent chance of developing cancer in their lifetime.
Many of these mutant p53 proteins acquire oncogenic properties that enable them to promot. Under stress conditions p53 must be activated to prohibit the replication of cells containing damaged DNA. Results revealed that mutation of p53 gene was found in 94 of 128 resected specimens of NSCLC including point mutations in 86 cases deletion and insertion in seven and mutation of the linking site in one and 639 percent of point mutations were G-T and T-G substitution and 256 percent G-A and A-G.
How mutations shape p53 interactions with the genome to promote tumorigenesis and drug resistance. These commonly include soft tissue and bone sarcomas breast and brain cancer adrenocortical tumors and leukemia and patients undergo frequent screening starting. Contrast this with the tumor suppressor BRCA1 which is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and can play a role in hereditary breast cancers Accordingly one of the ways by which mutations can cause p53 dysfunction is by a loss of DNA binding function.
The tumor suppressive transcription factor p53 regulates a wide array of cellular processes that confer upon cells an essential protection against cancer development. In fact these kinds of mutations can happen to anyone. P53 mutations in cancer.
If such cells continue to divide in an uncontrolled way they can lead to the formation of bladder cancer. That is the tumor suppressive effects of p53 are through transcription. P53 induces the transcription of genes that negatively regulate progression of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage or other cellular stressors and thus participates in maintaining genome stability.

The Consequences Of Somatic Tp53 Mutations In Tumorigenesis The Download Scientific Diagram
What Happens If The P53 Gene Mutates Quora
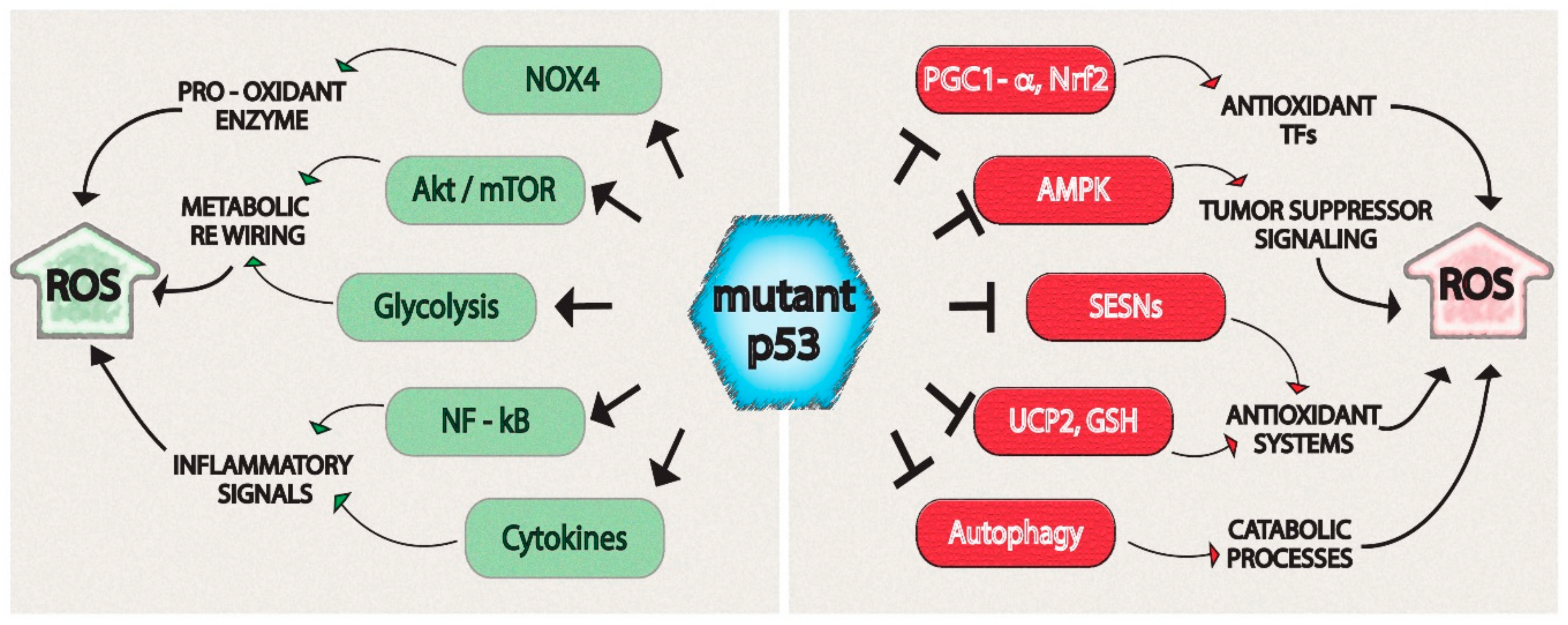
Biomolecules Free Full Text Mutant P53 Associated Molecular Mechanisms Of Ros Regulation In Cancer Cells Html

Comments
Post a Comment